On Balance Volume
On Balance Volume (OBV) is a popular technical analysis indicator used by traders and investors to measure buying and selling pressure in the stock market. Developed by Joseph Granville in the early 1960s, OBV helps traders identify potential trends and reversals by analyzing the relationship between volume and price movements.
On Balance Volume (OBV) is a popular technical analysis indicator used by traders and investors to measure buying and selling pressure in the stock market. Developed by Joseph Granville in the early 1960s, OBV helps traders identify potential trends and reversals by analyzing the relationship between volume and price movements. This guide will explain OBV in simple terms, how it’s calculated, and how traders use it to make informed decisions.
What is On Balance Volume (OBV)?
On Balance Volume is a momentum indicator that uses volume flow to predict changes in stock prices. The basic idea behind OBV is that volume precedes price movement. If a stock is experiencing increasing volume, it may indicate that the price will soon move up or down, depending on whether the volume is primarily buying or selling.
Why is OBV Important?
OBV is important because it helps traders:
- Identify Trends: Determine whether a stock is in an uptrend or downtrend based on volume movements.
- Spot Reversals: Recognize potential reversal points when the OBV diverges from price trends.
- Confirm Breakouts: Validate price breakouts or breakdowns by observing changes in volume.
How is OBV Calculated?
The calculation of On Balance Volume is straightforward and involves three main steps:
- Determine the Closing Price Change:
- If today’s closing price is higher than yesterday’s, add today’s volume to the OBV.
- If today’s closing price is lower than yesterday’s, subtract today’s volume from the OBV.
- If today’s closing price is the same as yesterday’s, the OBV remains unchanged.

- Day 1: OBV starts at 0 as the initial value.
- Day 2: Price increases; add volume (7000) to OBV, resulting in 7000.
- Day 3: Price decreases; subtract volume (6000) from OBV, resulting in 1000.
- Day 4: Price increases; add volume (8000) to OBV, resulting in 9000.
- Day 5: Price remains the same; OBV remains unchanged at 9000.
How to Interpret OBV
Interpreting OBV involves understanding the relationship between volume and price:
- Trend Confirmation:
- Rising OBV: Indicates that volume is increasing with price, suggesting a bullish trend. Traders often look for OBV to rise before taking long positions.
- Falling OBV: Indicates that volume is decreasing with price, suggesting a bearish trend. Traders may use falling OBV as a signal for short positions.
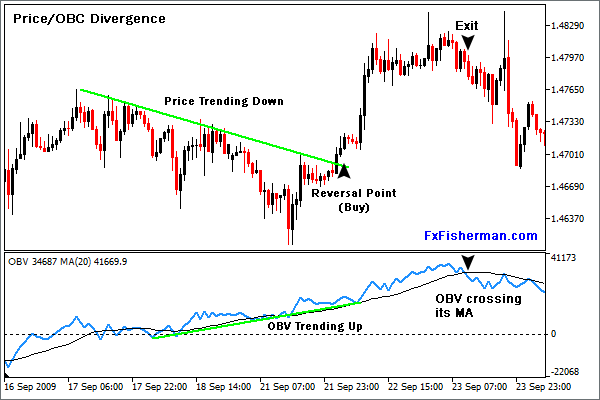
- Divergence:
- Bullish Divergence: Occurs when OBV is rising while the stock price is falling. This suggests that buying pressure is building up, potentially leading to a price reversal upwards.
- Bearish Divergence: Occurs when OBV is falling while the stock price is rising. This indicates selling pressure, potentially leading to a price reversal downwards.
- Breakout Confirmation:
- Price Breakout: When the price breaks through a resistance level, a rising OBV can confirm the breakout’s strength, suggesting the price may continue to rise.
- Price Breakdown: When the price falls below a support level, a falling OBV can confirm the breakdown’s strength, suggesting the price may continue to decline.

- Trend Confirmation: The rising OBV from Day 1 to Day 5 confirms a bullish trend as the price increases from $100 to $110.
- Bullish Divergence: If the price were to fall between Day 3 and Day 4 while OBV rises, it would indicate a bullish divergence, suggesting potential price recovery.
- Breakout Confirmation: The increase in OBV on Day 4 and Day 5 supports a breakout above a resistance level at $107.
How Traders Use OBV
Traders use OBV in various ways to make trading decisions:
- Identifying Trends: Traders look for consistent OBV trends to confirm whether the market is bullish or bearish.
- Spotting Divergence: Divergence between OBV and price can be a powerful signal for potential reversals, prompting traders to prepare for changes in market direction.
- Validating Breakouts: By confirming price movements with OBV, traders can be more confident in the strength of breakouts or breakdowns, reducing the risk of false signals.
- Volume Analysis: Traders analyze volume spikes in OBV to detect unusual buying or selling pressure, potentially indicating significant market moves.
Limitations of OBV
While OBV is a valuable tool, it does have its limitations:
- Lagging Indicator: OBV can lag behind actual price movements due to its reliance on volume data, potentially providing delayed signals.
- False Signals: Like any technical indicator, OBV can produce false signals, especially in choppy or sideways markets.
- Volume Accuracy: OBV assumes volume is accurately reported, which may not always be the case, leading to misleading analysis.
- Market Conditions: OBV may be less effective in highly volatile or thinly traded markets, where volume patterns are erratic.
How to Use OBV in Trading Strategies
OBV can be integrated into various trading strategies to enhance decision-making:
- OBV and Moving Averages:
- Combine OBV with moving averages to filter noise and identify trends more clearly.
- A crossover of OBV with a moving average can signal potential entry or exit points.
- OBV and Support/Resistance:
- Use OBV to confirm breakouts or breakdowns of key support and resistance levels.
- Rising OBV near resistance levels may indicate a strong breakout, while falling OBV near support levels may signal a breakdown.
- OBV and Divergence Strategy:
- Monitor for divergence between OBV and price to identify potential reversals.
- Confirm divergence signals with other indicators, such as RSI or MACD, for added reliability.
Conclusion
On Balance Volume (OBV) is a powerful technical analysis tool that provides insights into buying and selling pressure within the market. By understanding how OBV interacts with price, traders can enhance their ability to identify trends, spot reversals, and confirm breakouts.
Summary
- Purpose: Measures buying and selling pressure through volume analysis.
- Calculation: Cumulative volume based on price changes (add or subtract volume).
- Interpretation: Trend confirmation, divergence signals, breakout validation.
- Usage: Trend identification, divergence spotting, breakout validation.
- Limitations: Lagging indicator, false signals, volume accuracy issues.
By incorporating OBV into their trading strategies, traders can gain valuable insights into market dynamics and improve their overall trading performance.