Understanding Elliott Wave Theory
A Simple Guide to Understanding Elliott Wave Theory: How to Use It in Trading
Have you ever wondered why prices in the stock market seem to rise and fall in patterns that repeat themselves? This is where the Elliott Wave Theory comes into play. It’s a form of technical analysis that helps traders understand these price movements by identifying repeating wave patterns. If you’re new to trading or just curious about how the Elliott Wave Theory works, this guide is for you. We’ll break it down in simple terms, using examples and charts, so you can see how these waves can guide your trading decisions.
What is Elliott Wave Theory?
Elliott Wave Theory is a concept that suggests stock prices move in predictable patterns or “waves.” Developed by Ralph Nelson Elliott in the 1930s, this theory observes that market prices follow a specific pattern of movements that repeat over time. According to Elliott, these patterns can be seen in both short-term and long-term price charts, whether you’re looking at a single day of trading or several years.
The Basics of Elliott Wave Patterns
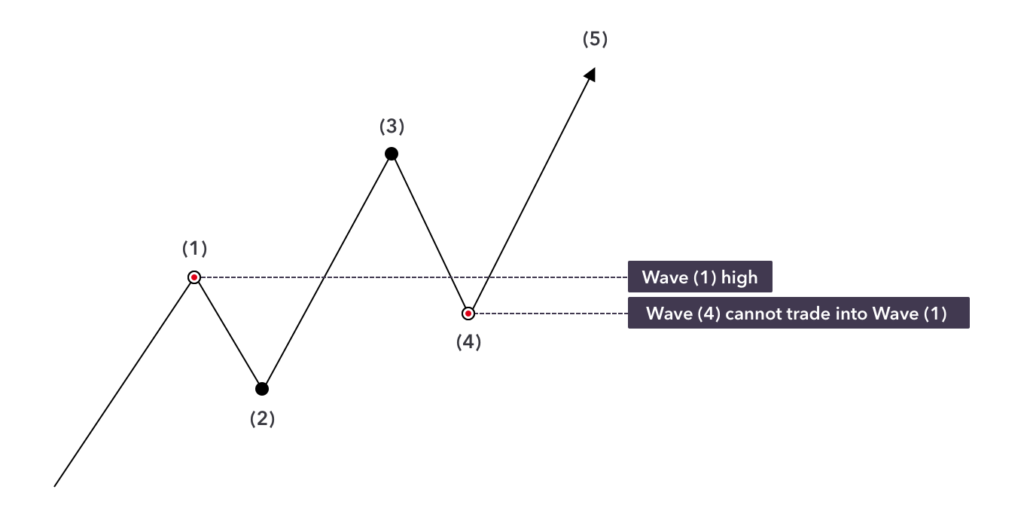
The Elliott Wave pattern is made up of a series of five waves in the direction of the main trend, followed by three corrective waves moving against the trend. Here’s a simple breakdown of how these waves work:
- Wave 1: The market moves up as buyers start entering, believing that the price is too low.
- Wave 2: Prices pull back slightly, but not enough to erase the previous gain. This happens as early buyers take profits, leading to a slight decline.
- Wave 3: The market surges again, typically the strongest and most significant upward move. This is when more traders recognize the trend and start buying, pushing prices higher.
- Wave 4: Another pullback occurs, often weaker than Wave 2. Some traders might take profits, but the overall sentiment remains bullish.
- Wave 5: The final push upwards as the last of the optimistic buyers enter the market, driving prices to a peak.
After these five waves, the market typically enters a corrective phase consisting of three waves:
- Wave A: A downward move as the market begins to correct.
- Wave B: A temporary upward movement, but it doesn’t reach the previous high.
- Wave C: A final move down, completing the correction.
The pattern then starts over again, with the next sequence of five waves and three corrective waves.
Why Do These Waves Occur?
The Elliott Wave Theory is based on crowd psychology. When investors feel optimistic about a stock, they buy, causing prices to rise. Conversely, when pessimism sets in, selling pressure leads to price declines. Elliott identified that these emotions create predictable patterns over time, forming the waves we see in the market.
Using Fibonacci Numbers with Elliott Wave
To make the Elliott Wave Theory even more precise, traders often use Fibonacci numbers. These numbers, which include ratios like 38%, 50%, and 61.8%, help predict where retracements (or pullbacks) in the market are likely to occur. The idea is that these Fibonacci retracement levels can serve as potential support or resistance points where the market might reverse direction.
For instance, after a wave moves up, a trader might expect the price to pull back to one of these Fibonacci levels before the next wave up begins. By combining Elliott Wave patterns with Fibonacci numbers, traders aim to make more informed decisions about when to enter or exit trades.
An Example Trade Using Elliott Wave Theory
Let’s walk through an example to illustrate how Elliott Wave Theory can be applied in real trading. Imagine you’re looking at a chart of the S&P 500, a popular stock market index, and you spot an Elliott Wave pattern forming.
Example Scenario:
- Wave 1 to Wave 2: The S&P 500 starts to rise, marking the first wave. You notice a slight pullback (Wave 2) and decide to watch for Wave 3.
- Wave 2 to Wave 3: The market rallies again, confirming the start of Wave 3, which is typically the longest and strongest wave. You decide to buy in anticipation of this upward movement.
- Wave 3 to Wave 4: As prices reach new highs, you anticipate a Wave 4 correction. You use Fibonacci retracement levels to identify a potential pullback level, such as the 38% retracement.
- Wave 4 to Wave 5: After the correction, Wave 5 begins. You might choose to ride this wave upwards or exit your position at a target profit level.
- Correction Waves (A, B, C): Following the completion of Wave 5, the market enters a corrective phase. You anticipate a downward move (Wave A), a partial rebound (Wave B), and a final move down (Wave C).
- Wave C Target: You identify a Fibonacci level where Wave C might end and consider entering a long position again for the next cycle of waves.
Chart Example:
This chart illustrates the Elliott Wave pattern applied to the S&P 500, showcasing how traders might use Fibonacci retracement levels to make informed trading decisions.
Making Profits with Elliott Wave
Trading using Elliott Wave Theory can be profitable if done correctly, but it’s important to remember that it’s not a foolproof strategy. Like any form of technical analysis, it comes with risks. Here are some practical tips for using Elliott Wave in trading:
- Identify the Correct Wave Count: One of the biggest challenges is correctly identifying which wave you are currently in. Misidentifying the wave count can lead to poor trading decisions.
- Use Stop Losses: Always set stop losses to protect your capital in case the market moves against your predictions. This helps manage risk and minimize potential losses.
- Combine with Other Indicators: While Elliott Wave Theory is powerful on its own, combining it with other technical indicators like moving averages or MACD can provide additional confirmation for your trades.
- Stay Updated with Market News: Be aware of major economic events and news that might influence market trends. Market sentiment can quickly change due to news, impacting the accuracy of Elliott Wave predictions.
Where to Trade Using Elliott Wave Theory
If you’re interested in trying out Elliott Wave Theory, you can start trading on platforms that offer technical analysis tools. Brokers like Pepperstone provide access to various markets, including forex, stocks, and indices, where you can apply these principles. However, remember that trading involves risk, and it’s important to practice with a demo account before investing real money.
Further Reading
Elliott Wave Theory can seem complex at first, but with practice and patience, it can become a valuable tool in your trading toolkit. If you want to dive deeper into this topic, consider exploring resources like books or online courses that cover advanced wave patterns and strategies.
In conclusion, Elliott Wave Theory offers a unique perspective on market behavior, helping traders anticipate price movements by recognizing repeating patterns. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced trader, understanding these waves can enhance your trading strategy and potentially lead to better trading outcomes. Keep in mind that no strategy is without risk, and continuous learning and practice are key to mastering the art of trading with Elliott Wave Theory.
I will code your US stocks, options or futures trading bot. Click here