Mass Index
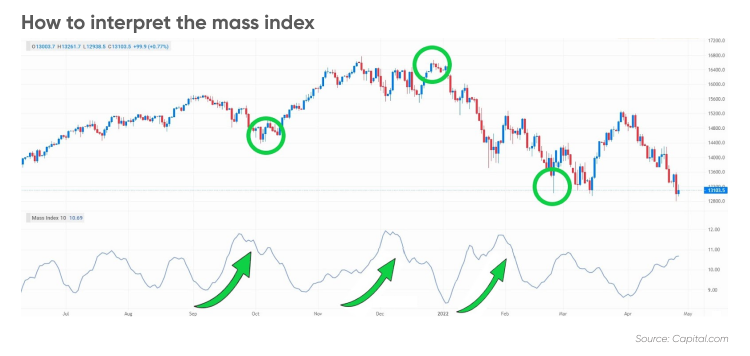
The Mass Index calculates the “mass” of price movements by analyzing the difference between the high and low prices over a specific period. It then applies exponential moving averages to smooth the results. When the Mass Index rises above a certain threshold, it suggests that the price is compressing, indicating a potential trend reversal or significant price movement.
Traders often use the Mass Index in conjunction with other indicators to make trading decisions. A rising Mass Index may indicate that a price breakout or trend reversal is imminent, while a declining Mass Index may suggest a period of price stability.
As with any technical indicator, the Mass Index should be used alongside other analysis tools and methods to validate signals and improve the accuracy of trading decisions. It is essential to practice and test the indicator in a demo or paper trading environment before applying it to real trades and use proper risk management techniques to protect capital from potential losses.
How to Buy and Sell Using Mass Index?
Buying and selling using the Mass Index involves a combination of the indicator’s signals and price analysis. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Buying using Mass Index:
- Plot the Mass Index: Set up your trading platform to display the Mass Index indicator on the price chart of the asset you want to trade.
- Identify Compression Periods: Look for periods when the Mass Index rises above a certain threshold, indicating price compression and potential trend reversal.
- Confirm Price Patterns: Use the Mass Index in combination with other technical indicators and price patterns to confirm potential entry points. Look for bullish signals, such as breakouts from chart patterns or support levels.
- Entry Point: Consider entering a long position when the Mass Index suggests price compression, and the price confirms a bullish trend continuation or reversal.
Selling using Mass Index:
- Analyze Compression Periods: Observe the Mass Index for declining values, indicating decreased price volatility and stability.
- Look for Reversal Signals: Pay attention to potential trend reversal signals when the Mass Index declines significantly after a period of compression.
- Confirm Price Patterns: Use the Mass Index alongside other technical indicators and price patterns to confirm potential exit points. Look for bearish signals, such as breakdowns from chart patterns or resistance levels.
- Exit Point: Consider exiting a long position or entering a short position when the Mass Index suggests decreased volatility, and the price indicates a bearish trend continuation or reversal.
- Risk Management: Always apply proper risk management techniques, such as setting stop-loss orders, to protect your capital from significant losses.
Remember that the Mass Index is not a standalone tool and should be used in conjunction with other analysis methods for more reliable trading decisions. Additionally, practice using the Mass Index in a demo account or paper trading before applying it to real trades.
Pros and Cons
Pros of Mass Index:
- Volatility Indicator: The Mass Index helps traders identify periods of price compression and potential trend reversals, aiding in better market timing.
- Early Warning Signals: It can provide early warning signals of possible trend changes or significant price movements, helping traders stay ahead of the market.
- Simple to Use: The Mass Index is relatively easy to interpret, making it accessible to traders of all experience levels.
- Confirmation Tool: When used with other indicators and analysis methods, the Mass Index can confirm potential entry and exit points, enhancing trading accuracy.
Cons of Mass Index:
- Lagging Indicator: Like many technical indicators, the Mass Index relies on historical data, which means it may lag behind the most current price movements.
- False Signals: As with any indicator, the Mass Index can generate false signals, leading to potential trading losses if used in isolation.
- Subjective Threshold Setting: The choice of threshold for defining price compression can be subjective, leading to different interpretations and potential inconsistencies.
- Not Standalone: The Mass Index should be used alongside other analysis tools and methods to validate signals and improve the accuracy of trading decisions.
As with any technical indicator, the Mass Index is not foolproof and should be used in combination with other tools and analysis techniques. Traders should also practice risk management and thoroughly test their strategies before applying them to real trading scenarios.